The Ultimate SSAT Lower Level Math Formula Cheat Sheet

If you’re taking the SSAT Lower Level Math test in a few weeks or months, you might be anxious about how to remember ALL the different formulas and math concepts and recall them during the test.
The SSAT Lower Level Math covers a wide range of topics—from as early as elementary school all the way to high school.
While you have probably learned many of these formulas at some point, it may have been a long time since you’ve actually used them. This is where most test takers have a hard time preparing for the test.
So, what formulas do you need to have memorized for the SSAT Lower Level Math before the test day?
Following is a quick formula reference sheet that lists all important SSAT Lower Level Math formulas you MUST know before you sit down for the test.
If you learn every formula in this SSAT Lower Level Math Formula Cheat Sheet, you will save yourself valuable time on the test and probably get a few extra questions correct.
Looking for a comprehensive and complete list of all SSAT Lower Level Math formulas? Please have a look at SSAT Lower Level Math Formulas
The Absolute Best Book to Ace the SSAT Lower Level Math Test
SSAT Lower Level Math Cheat Sheet
Fractions
A number expressed in the form \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Adding and Subtracting with the same denominator:
\(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{b}=\frac{a+c}{b}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}-\frac{c}{b}=\frac{a-c}{b}\)
Adding and Subtracting with the different denominator:
\(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{d}=\frac{ad+cb}{bd}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}-\frac{c}{d}=\frac{ad-cb}{bd}\)
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions:
\(\frac{a}{b} × \frac{c}{d}=\frac{a×c}{b×d}\)
\(\frac{a}{b} ÷ \frac{c}{d}=\frac{\frac{a}{b}}{\frac{c}{d}}=\frac{ad}{bc}\)
Decimals
Is a fraction written in a special form? For example, instead of writing \(\frac{1}{2}\) you can write \(0.5\).
Mixed Numbers
A number is composed of a whole number and a fraction. Example: \(2 \frac{2}{ 3}\) Converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers: \(a \frac{c}{b}=a+\frac{c}{b}= \frac{ab+ c}{b}\)
Factoring Numbers
Factor a number means breaking it up into numbers that can be multiplied together to get the original number. Example:\(12=2×2×3\)
Integers
\( \{…,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,…\} \)
Includes: zero, counting numbers, and the negative of the counting numbers
Real Numbers
All numbers that are on a number line. Integers plus fractions, decimals, and irrationals, etc.) (\(\sqrt{2},\sqrt{3},π\), etc.)
Order of Operations
PEMDAS
(parentheses/ exponents/ multiply/ divide/ add/ subtract)
Absolute Value
Refers to the distance of a number from, the distances are positive as the absolute value of a number cannot be negative. \(|-22|=22\)
Ratios
A ratio is a comparison of two numbers by division. Example: \(3 : 5\), or \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Percentages
Use the following formula to find part, whole, or percent
part \(=\frac{percent}{100}×whole\)
Proportional Ratios
A proportion means that two ratios are equal. It can be written in two ways:
\(\frac{a}{b}=\frac{c}{d}\) , \(a: b = c: d \)
Percent of Change
\(\frac{New \ Value \ – \ Old \ Value}{Old Value}×100\%\)
Expressions and Variables
A variable is a letter that represents unspecified numbers. One may use a variable in the same manner as all other numbers: Addition: \(2+a\): \(2\) plus a
Subtraction: \(y-3\) : \(y\) minus \(3\)
Division: \(\frac{4}{x}\) : 4 divided by x
Multiplication: \(5a\) : \(5\) times a
Distributive Property
\(a(b+c)=ab+ac\)
Equations
The values of the two mathematical expressions are equal.
\(ax+b=c\)
Distance from A to B:
\(\sqrt{(x_{1}-x_{2})^2+(y_{1}-y_{2})^2 }\)
Parallel and Perpendicular lines:
Parallel lines have equal slopes. Perpendicular lines (i.e., those that make a \(90^° \) angle where they intersect) have negative reciprocal slopes: \(m_{1}\) .\(m_{2}=-1\).
Parallel Lines (l \(\parallel\) m)
Mid-point of the segment AB:
M (\(\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}}{2} , \frac{y_{1}+y_{2}}{2}\))
Slope of the line:
\(\frac{y_{2}- y_{1}}{x_{2} – x_{1} }=\frac{rise}{run}\)
Point-slope form:
Given the slope m and a point \((x_{1},y_{1})\) on the line, the equation of the line is
\((y-y_{1})=m \ (x-x_{1})\).
Slope-intercept form:
given the slope m and the y-intercept b, then the equation of the line is:
\(y=mx+b\).
Factoring:
“FOIL”
\((x+a)(x+b)\)
\(=x^2+(b+a)x +ab\) “Difference of Squares”
\(a^2-b^2= (a+b)(a-b)\)
\(a^2+2ab+b^2=(a+b)(a+b) \)
\(a^2-2ab+b^2=(a-b)(a-b)\) “Reverse FOIL”
\(x^2+(b+a)x+ab=\) \((x+a)(x+b)\)
Exponents:
Refers to the number of times a number is multiplied by itself.
\(8 = 2 × 2 × 2 = 2^3\)
Scientific Notation:
It is a way of expressing numbers that are too big or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form.
In scientific notation all numbers are written in this form: \(m \times 10^n\)
Scientific notation:
\(5×10^0\)
\(-2.5×10^4\)
\(5×10^{-1}\)
\(2,122456×10^3\)
Square:
The number we get after multiplying an integer (not a fraction) by itself. Example: \(2×2=4,2^2=4\)
Square Roots:
A square root of \(x\) is a number r whose square is \(x: r^2=x\)
\(r\) is a square root of \(x\)
Pythagorean Theorem:
\(a^2+b^2=c^2\)
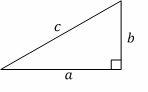
Triangles
All triangles:
Area \(=\frac{1}{2}\) b . h
Angles on the inside of any triangle add up to \(180^\circ\).
Equilateral:
These triangles have three equal sides, and all three angles are \(60^\circ\).
Isosceles:
An isosceles triangle has two equal sides. The “base” angles (the ones opposite the two sides) are equal (see the \(45^\circ\) triangle above).
Circles
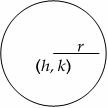
Area \(=πr^2\)
Circumference \(=2πr\)
Full circle \(=360^\circ\)
Rectangles
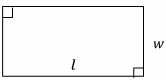
(Square if l=w)
Area=lw
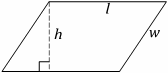
Parallelogram
(Rhombus if l=w)
Area=lh
Regular polygons are n-sided figures with all sides equal and all angles equal.
The sum of the inside angles of an n-sided regular polygon is
\((n-2) .180^\circ\).
Area of a trapezoid:
\(A =\frac{1}{2} h (b_{1}+b_{2})\)
Surface Area and Volume of a Rectangular/right prism:
\(SA=ph+2B\)
\(V=Bh\)
Surface Area and Volume of a Cylinder:
\(SA =2πrh+2πr^2\)
\(V =πr^2 h \)
Surface Area and Volume of a Cone
\(SA =πrs+πr^2\)
\(V=\frac{1}{3} \ πr^2 \ h\)
Surface Area and Volume of a Sphere
\(SA =4πr^2\)
\(V =\frac{4}{3} \ πr^3\)
(p \(=\) perimeter of base B; \(π ~ 3.14 \))
Simple interest:
\(I=prt\)
(I = interest, p = principal, r = rate, t = time)
mean:
mean: \(\frac{sum \ of \ the \ data}{of \ data \ entires}\)
mode:
value in the list that appears most often
range:
largest value \(-\) smallest value
Median
The middle value in the list (which must be sorted)
Example: median of
\( \{3,10,9,27,50\} = 10\)
Example: median of
\( \{3,9,10,27\}=\frac{(9+10)}{2}=9.5 \)
Average
\( \frac{sum \ of \ terms}{number \ of \ terms}\)
Average speed
\(\frac{total \ distance}{total \ time}\)
Probability
\(\frac{number \ of \ desired \ outcomes}{number \ of \ total \ outcomes}\)
The probability of two different events A and B both happening is:
P(A and B)=p(A) .p(B)
as long as the events are independent (not mutually exclusive).
Powers, Exponents, Roots
\(x^a .x^b=x^{a+b}\)
\(\frac{x^a}{x^b} = x^{a-b}\)
\(\frac{1}{x^b }= x^{-b}\)
\((x^a)^b=x^{a.b}\)
\((xy)^a= x^a .y^a\)
\(x^0=1\)
\(\sqrt{xy}=\sqrt{x} .\sqrt{y}\)
\((-1)^n=-1\), if n is odd.
\((-1)^n=+1\), if n is even.
If \(0<x<1\), then
\(0<x^3<x^2<x<\sqrt{x}<\sqrt{3x}<1\).
Simple Interest
The charge for borrowing money or the return for lending it.
Interest = principal \(×\) rate \(×\) time
OR
\(I=prt\)
Powers/ Exponents
Positive Exponents
An exponent is simply shorthand for multiplying that number of identical factors. So \(4^3\) is the same as (4)(4)(4), three identical factors of 4. And \(x^3\) is just three factors of x, \((x)(x)(x)\).
Negative Exponents
A negative exponent means to divide by that number of factors instead of multiplying.
So \(4^{-3}\) is the same as \( \frac{1}{4^3}\) and
\(x^{-3}=\frac{1}{x^3}\)
Factorials
Factorial- the product of a number and all counting numbers below it.
8 factorial \(=8!=\)
\(8×7×6×5×4×3×2×1=40,320\)
5 factorial \(=5!=\)
\(5×4×3×2×1=120\)
2 factorial \(=2!=2× 1=2\)
Multiplying Two Powers of the SAME Base
When the bases are the same, you find the new power by just adding the exponents
\(x^a .x^b=x^{a+b }\)
Powers of Powers
For the power of power: you multiply the exponents.
\((x^a)^b=x^{(ab)}\)
Dividing Powers
\(\frac{x^a}{x^b} =x^a x^{-b}= x^{a-b}\)
The Zero Exponent
Anything to the 0 power is 1.
\(x^0= 1\)
The Best Books to Ace the SSAT Lower Level Math Test
Related to This Article
More math articles
- Everything You Need to Know about Indeterminate and Undefined Limits
- CLEP College Algebra FREE Sample Practice Questions
- How to Solve Point-Slope Form of Equations?
- Ratio, Proportion and Percentages Puzzle – Challenge 29
- SAT Math Formulas
- Algebra Puzzle – Critical Thinking 14
- 5th Grade ACT Aspire Math Practice Test Questions
- Infinitely Close But Never There
- 7th Grade IAR Math FREE Sample Practice Questions
- 3rd Grade STAAR Math FREE Sample Practice Questions










What people say about "The Ultimate SSAT Lower Level Math Formula Cheat Sheet - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.