How to Divide Polynomials Using Long Division?
Long division of polynomials is the process of dividing one polynomial into another polynomial. In this article, let's familiarize ourselves with dividing polynomials using long division.

Related Topics
A step-by-step guide to dividing polynomials using long division
A long-division polynomial is an algorithm for dividing a polynomial into another polynomial of the same or lower degree.
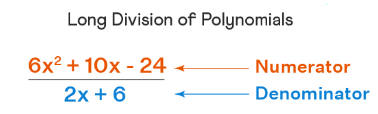
The long division of polynomials also consists of a divisor, a quotient, a dividend, and a remainder.
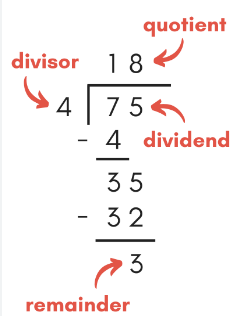
The following are the steps for the long division of polynomials:
- Step 1. Sort the terms in decreasing order of their indices (if needed). Write the missing terms with a coefficient of zero.
- Step 2. For the first term of the quotient, divide the first term of the dividend by the first term of the divisor.
- Step 3. Multiply this quotient statement by the divisor to get the product.
- Step 4. Subtract this product from the dividend and drop the next term (if any). The difference and the brought-down term will form the new dividend.
- Step 5. Follow this process until you get a remainder, which can be zero or an index less than the divisor.
Related to This Article
More math articles
- Pre-Algebra Worksheets: FREE & Printable (Updated for 2024)
- How to Use Measures of Center and Spread to Compare Populations
- Space Station Canteen: A Guide How to Estimate the Amount of a Tip
- Full-Length 6th Grade SBAC Math Practice Test-Answers and Explanations
- How to Choose a Model to Subtract Fractions with Like Denominators
- Ambiguous No More: The L’Hôpital’s Rule
- 7th Grade FSA Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- A Deep Dive Into the World Derivative of Polar Coordinates
- 10 Most Common 6th Grade OST Math Questions
- 10 Famous Math Problems and the History Behind Them



















What people say about "How to Divide Polynomials Using Long Division? - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.