Full-Length CLEP College Algebra Practice Test-Answers and Explanations

Did you take the CLEP College Algebra Practice Test? If so, then it’s time to review your results to see where you went wrong and what areas you need to improve.
CLEP College Algebra Mathematical Reasoning Practice Test Answers and Explanations
1- Choice C is correct
\((6m^2-4m-8)+(12m+5)\), Add like terms together: \(-4m+12m=8m 6m^2\) doesn’t have like terms. \(-8+5=-3\), Combine these terms into one expression to find the answer:\( 6m^2+8m-3\)
2- Choice E is correct
Method 1: Plugin the values of \(x\) and y provided in the options into both equations.
A. \((-2,1) x-y=2→-2-1=-3≠2 \)
B.\( (1,2) x-y=2→1-2=-1≠2 \)
C. \((2,5) x-y=2→2-5=-3≠2 \)
D. \((4,8) x-y=2→4-8=-4≠2 \)
E. \((6,4) x-y=2→6-4=2 \)
Only option E is correct. Method 2: Multiplying each side of \(x-y=2\) by 3 gives \(3x-3y=6\). Then, adding the corresponding side of \(3x-3y=6\) and \(5x+3y=42\) gives \(8x=48\). Dividing each side of \(8x=48\) by 8 gives \(x=6\). Finally, substituting 6 for \(x\) in \(x-y=2\), or \(y=6-2=4\). Therefore, the solution to the given system of equations is (6,4).
3- Choice E is correct
If \(f(x)=x^2+8x+28\), then find \(f(-2x)\) by substituting \(-2x\) for every \(x\) in the function. This gives: \(f(-2x)=(-2x)^2+8(-2x)+28\), It simplifies to: \(f(-2x)=4x^2-16x+28\)
4- Choice C is correct
First, find the equation of the line. All lines through the origin are of the form \(y=mx\), so the equation is \(y=3x\). Of the given choices, only choice C (9,3), satisfies this equation:
\(y=3x→3=3(1)=3\)
5- Choice C is correct
Add 5 both sides of the equation \(6x-5=37\) gives \(6x=37+5=42\). Dividing each side of the equation \(6x=42\) by 6 gives \(x=7\). Substituting 7 for \(x\) in the expression \(3x+12\) gives\(3(7)+12=33.\)
6- Choice B is correct
The input value is 2. Then: \(x=2 f(x)=2x^2+4x-8→ f(2)=2(2^2 )+4(2)-8=8+8-8=8\)
7- Choice A is correct
To rewrite \(\frac{1}{\frac{1}{x+2}+\frac{1}{x-3}}\), first simplify \(\frac{1}{x+2}+\frac{1}{x-3}\).
\(\frac{1}{x+2}+\frac{1}{x-3}=\frac{1(x-3)}{(x+2)(x-3)}+\frac{1(x+2)}{(x-3)(x+2)}=\frac{(x-3)+(x+2)}{(x+2)(x-3)}\)
Then: \(\frac{1}{\frac{1}{x+2}+\frac{1}{x-3}}=\frac{1}{\frac{(x-3)+(x+2)}{(x+2)(x-3)}}=\frac{(x+2)(x-3)}{(x-3)+(x+2)}\). (Remember, \(\frac{1}{\frac{1}{x}}=x\))
This result is equivalent to the expression in choice A.
8- Choice A is correct
Since (0, 0) is a solution to the system of inequalities, substituting 0 for \(x\) and 0 for \(y\) in the given system must result in two true inequalities. After this substitution, \(y > a+x\) becomes \(0 > a\), and \(y < x+b\) becomes \(0< b\). Hence, \(a\) is negative and \(b\) is positive. Therefore, \(a<b\).
9- Choice D is correct
First find the slope of the line using the slope formula. \(m=\frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1 }\)
Substituting in the known information. \((x_1, y_1 )=(1,4), (x_2,y_2 )=(3,6) m=\frac{6-4}{3-1}=\frac{2}{2}=1\).
Now the slope to find the equation of the line passing through these points. \(y=mx+b \)
Choose one of the points and plug in the values of \(x\) and y in the equation to solve for b. Let’s choose points (1, 4). Then:
\(y=mx+b→4=1(1)+b→4=1+b→b=4-1=3 \)
The equation of the line is: \(y=x+3 \)
Now, plug in the points provided in the choices into the equation of the line.
A. \((-2,4) y=x+3→4=-2+3→4=1\) This is NOT true.
B. \((-1,0) y=x+3→0=-1+3→0=2\) This is NOT true.
C. \((0,0) y=x+3→0=0+3→0=3\) This is NOT true.
D. \((1,4) y=x+3→4=1+3→4=4\) This is true!
E. \((4,1) y=x+3→1=4+3→1=7\) This is NOT true.
Therefore, the only point from the choices that lie on the line is (1,4).
10- Choice C is correct
You can find the possible values of a and b in \((ax+2)(bx+6)\) by using the given equation\( a+b=12\) and finding another equation that relates the variables a and b. Since\( (ax+2)(bx+6)=32x^2+cx+12\), expand the left side of the equation to obtain.
\(abx^2+6ax+2bx+12=32x^2+cx+12 \)
Since ab is the coefficient of \(x^2\) on the left side of the equation and 32 is the coefficient of \(x^2\) on the right side of the equation, it must be true that \(ab=32\)
The coefficient of \(x\) on the left side is \(6a+2b\) and the coefficient of \(x\) in the right side is c. Then:
\(6a+2b=c, a+b=12\), then: \(a=12-b\), Now, plug in the value of a in the equation \(ab=32\). Then: \(ab=32\)\(→(12-b)b=32→12b-b^2=32 \)
Add\( -12b+b^2\) both sides. Then: \(b^2-12b+32=0 \)
Solve for b using the factoring method. \(b^2-12b+32=0→(b-4)(b-8)=0\) Thus, either \(b=4\) and \(a=8\), or \(b =8\) and \(a=4\).
If \(b= 4\) and \(a=8\), then ,\(6a+2b=c→6(8)+2(4)=c→c=48+8=56\)
If \(b=8\) and\( a=4\), then, \(6a+2b=c→6(4)+2(8)=c→c=24+16=40 \)
Therefore, the two possible values for c are 56 and 40.
11- Choice D is correct
\(|2x+6|≤2→-2≤2x+6≤2→-2-6≤2x+6-6≤2-6→-8≤2x≤-4 → -4≤x≤-2\)
12- Choice E is correct
Multiplying each side of \(\frac{7}{2x}=\frac{8}{2x+1}\) by \(2x(2x+1)\) gives \(7(2x+1)=16(x)→14x+7=16x →16x-14x=7 →2x=7 →x=\frac{7}{2}\) , Therefore, the value of \(2x=2(\frac{7}{2})=7\).
13- Choice C is correct
The equation of a circle can be written as \((x-h)^2+(y-k)^2=r^2\) where (h,k) are the coordinates of the center of the circle and r is the radius of the circle. Since the coordinates of the center of the circle are \((2,-1)\), the equation is \((x-2)^2+(y+1)^2=r^2\), where r is the radius. The radius of the circle is the distance from the center \((2,-1)\), to the given endpoint of a radius, \((4,-1)\). By the distance formula, \(r^2=(4-2)^2+(-1+1)^2=2^2=4 \)Therefore, an equation of the given circle is \((x-2)^2+(y+1)^2=4\)
14- Choice A is correct
To figure out what the equation of the graph is, first find the vertex. From the graph, we can determine that the vertex is at (2, 17). We can use vertex form to solve the equation of this graph. Recall vertex form,\( y=a(x-h)^2+k\), where \(h\) is the \(x\) coordinate of the vertex, and k is the \(y\) coordinate of the vertex. Plugging in our values, you get \(y=a(x-2)^2+17\) To solve for a, we need to pick a point on the graph and plug it into the equation.
Let’s pick (0,1). \(1=a(0-2)^2+17→1=a(-2)^2+17→1=4a+17 1-17=4a →-16=4a→a=-4\), Now the equation is : \(y=-4(x-2)^2+17\) Let’s expand this, \(y=-4(x^2-4x+4)+17→y=-4x^2+16x-16+17→ y=-4x^2+16x+1 \)
The equation in Choice A is the same.
15- Choice B is correct
To solve this problem, first recall the equation of a line: \(y=mx+b\) Where m=slope
\(y=y\)-intercept, Remember that slope is the rate of change that occurs in a function and that the y-intercept is the y value corresponding to \(x=0\). Since the height of John’s plant is 8 inches tall when he gets it. Time (or \(x\)) is zero. The plant grows 5 inches per year. Therefore, the rate of change of the plant’s height is \(5\). The \(y\)-intercept represents the starting height of the plant which is 8 inches.
16- Choice E is correct
\(x^2-10x-r=(x+5)(x-p)=x^2+(5-p)x-5p\)
On the left side of the equation the coefficient of \(x\) is \(-10\) and on the right side of the equation the coefficient of \(x\) is 5-p. Thus \(5-p=-10→p=15\) and \(r=5p=5(15)=75\)
17- Choice A is correct
Subtracting 6 to each side of the inequality \(6n+4≥2\) yields the inequality \(6n-2≥ -4\). Therefore, the least possible value of \(6n-2 is -4\).
18- Choice D is correct
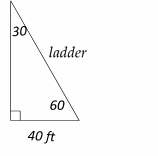
The relationship among all sides of a special right triangle
30\(^\circ\)-60\(^\circ\)- 90\(^\circ\) is provided in this triangle:
In this triangle, the opposite side of the 30\(^\circ\) angle is half of the hypotenuse.
Draw the shape of this question: The ladder is the hypotenuse.
Therefore, the ladder is 80 ft.
19- Choice B is correct
The intersection of A and B is A\(∩\)B={1,15}. There are 2 elements in A\(∩\)B.
20- Choice B is correct
The intersection of A and B is: A\(∩\)B={2,4,6}
The union of (A\(∩\)B) and C is: (A\(∩\)B)\(∪\)C={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,9,11}
The Absolute Best Book to Ace the CLEP College Algebra Math Test
21- Choice C is correct
If the value of \(|x+6|+6\) is equal to 0, then \(|x+6|+6=0\). Subtracting 6 from both sides of this equation gives \(|x+6|=-6\). The expression \(|x+6|\) on the left side of the equation is the absolute value of \(x+6\), and the absolute value can never be a negative number.
Thus \(|x+6|=-6\) has no solution. Therefore, there are no values for \(x\) for which the value of \(|x+6|+6\) is equal to 0.
22- Choice D is correct
The speed of car A is 68 mph and the speed of car B is 76 mph. When both cars drive in a straight line toward each other, the distance between the cars decreases at the rate of 144 miles per hour: \(68+72=144 \)
40 minutes is two-thirds of an hour. Therefore, they will be 96 miles apart 40 minutes before they meet. \(\frac{2}{3}×144=96\)
23- Choice C is correct
First calculate the Vertex point:\(f(x)=-x^2+3x-4→a=-1,b=3,c=-4.x=\frac{-b}{2a}=\frac{-3}{-2}=\frac{3}{2}\)
Then \(y=-(\frac{3}{2})^2+3(\frac{3}{2})-4=-\frac{9}{4}+\frac{9}{2}-4=\frac{-9+18-16}{4}=\frac{-7}{4}\). Thus maximum point is \((\frac{3}{2},-\frac{7}{4}. (-1))\)and 4 are minimum points in this function. If \(x=-1\) or \(x=4 ,y=-8\).thus minimum points are\( (-1,-8)\) and\( (4,-8)\).The ratio of minimum to maximum of this function is :\(\frac{-8}{\frac{-7}{4}}=\frac{-8×4}{-7}=\frac{32}{7}\)
24- Choice A is correct
There can be 0, 1, or 2 solutions to a quadratic equation. In standard form, a quadratic equation is written as: \(ax^2+bx+c=0\), For the quadratic equation, the expression \(b^2-4ac \)is called the discriminant. If the discriminant is positive, there are 2 distinct solutions for the quadratic equation. If the discriminant is 0, there is one solution for the quadratic equation and if it is negative the equation does not have any solutions. To find number of solutions for \(2x^2=x-3\), first, rewrite it as \(2x^2-x+3=0\). Find the value of the discriminant. \(b^2-4ac=(-1)^2-4(2)(3)=1-24=-23\), Since the discriminant is negative, the quadratic equation does not have any solutions.
25- Choice D is correct
\(x^2+6x^4-7y^3+4z^2-4x^4+5y^3-4z^2+y^2-z=(6x^4-4x^4 )+(-7y^3+5y^3 )+(4z^2-4z^2 )+x^2+y^2-z=2x^4-2y^3+x^2+y^2-z\)
26- Choice D is correct
Solve for\( x\).
\(x^3+18=130\)
\(x^3=112 \)
Let’s review the choices.
A. 1 and \(2. 13 = 1\) and \(23 = 8, 112\) is not between these two numbers.
B. 2 and \(3. 23 = 8\) and \(33 = 27, 112\) is not between these two numbers.
C. 3 and \(4. 33 = 27\) and \(43 = 64, 112\) is not between these two numbers.
D. 4 and \(5. 43 = 64\) and \(53 = 125, 112\) is between these two numbers.
E. 5 and \(6. 53 = 125\) and\( 63 = 216, 112\) is not between these two numbers.
27- Choice C is correct
In the figure angle A is labeled \((2x-4)\) and it measures 42. Thus, \(2x-4=42\) and \(2x=46\) or \(x=23\). That means that angle B, which is labeled \((4x-9)\), must measure \((4×23)-9=92-9=83\). Since the three angles of a triangle must add up to \(180, 42+83+y+4=180\), then: \(y+4=55→y=55-4=51\)
28- Choice C is correct
Four years ago, Amy was two times as old as Mike. Mike is 12 years old now. Therefore, 4 years ago Mike was 8 years. Four years ago, Amy was: A\(=8×2=16\), Now Amy is 20 years old: \(16+4=20\)
29- Choice C is correct
\(8\%\) of the volume of the solution is alcohol. Let \(x\) be the volume of the solution. Then: \(8\%\) of \(x=36\) ml⇒ \(0.08x=36 ⇒ x=36÷0.08=450\)
30- Choice A is correct
I. \(|a|<1→-1<a<1\)
Multiply all sides by b. Since, \(b>0→-b<ba<b\) (it is true!)
II. Since, \(-1<a<1 , a<0→-a>a^2>a \) (plug in \(\frac{-1}{2}\), and check!) (It’s false)
III. \(-1<a<1\),multiply all sides by 3,then: \(-3<3a<3\)
Subtract 2 from all sides. Then: \(-2-3<3a-2<3-2→-5<3a-2<1\) (It is NOT true!)
31- Choice E is correct
Subtracting \(4x\) and 2 to both sides of \(4x+2≥5x-4\) gives \(6≥x\). Therefore, \(x\) is a solution to \(4x+2≥5x-4\) if and only if \(x\) is less than or equal to 6 and \(x\) is NOT a solution to \(4x+2≥5x-4\) if and only if \(x\) is greater than 6. Of the choices given, only 8 is greater than 6 and, therefore, cannot be a value of \(x\).
32- Choice C is correct
\((x+2)^4=256→x+2=4→x=4-2=2, →(x+5)(x-1)=(2+5)(2-1)=(7)(1)=7\)
33- Choice D is correct
We know that: \(i=\sqrt{-1}⇒i^2=-1,
(2+4i)(3-3i)=6-6i+12i-12i^2=6+6i+12=6i+18\)
34- Choice A is correct
Substituting 3 for \(x\) and 9 for y in \(y=nx-3\) gives \(9=(n)(3)-3\), which gives \(n=4\). Hence, \(y=4x-3\). Therefore, when \(x= 2\), the value of \(y\) is \(y=(4)(2)-3=5\).
35- Choice A is correct.
Solve for \(x. \frac{4x}{15}=\frac{x-3}{5}\). Multiply the second fraction by 3. \(\frac{4x}{15}=\frac{3(x-3)}{5×3}\)
Two denominators are equal. Therefore, the numerators must be equal.
\(4x=3x-9 \)
\(4x-3x=-9 \)
\(x=-9\)
36- Choice A is correct
Let \(x\) be the number of years. Therefore, $12,000 per year equals \(12000x\). starting from $36,000 annual salary means you should add that amount to \(12000x\). Income more than that is: \(I>12000x+36000\)
37- Choice E is correct
First square both sides of the equation to get \(3m-2=m^2 \)
Subtracting both sides by \(3m-2\) gives us the equation \(m^2-3m+2=0 \)
Here you can solve the quadratic equation by factoring to get \((m-1)(m-2)=0 \)
For the expression \((m-1)(m-2)\) to equal zero, \(m=1\) or \(m=2\)
38- Choice B is correct
To solve the equation for \(y\), multiply both sides of the equation by the reciprocal of \(\frac{8}{3}\) , which is \(\frac{3}{8}\) , this gives \((\frac{3}{8})×\frac{8}{3} y=\frac{16}{12}×(\frac{3}{8})\), which simplifies to \(y=\frac{16×3}{12×8}=\frac{1}{2}\).
39- Choice C is correct
Let L be the length of the rectangular and W be the width of the rectangular. Then, \(L=2W+3\) The perimeter of the rectangle is 36 meters. Therefore: \(2L+2W=24, L+W=12 \)
Replace the value of L from the first equation into the second equation and solve for \(W: (2W+3)+W=12→3W+3=12→3W=9→W=3\), The width of the rectangle is 3 meters and its length is: \(L=2W+3=2(3)+3=9,\) The area of the rectangle is: length \(×\) width:\(9×3=27\)
40- Choice E is correct
Given the two equations, substitute the numerical value of an into the second equation to solve for \(x. a=\sqrt{7}, 5a=\sqrt{5x}\), Substituting the numerical value for an into the equation with \(x\) is as follows. \(5(\sqrt{7})=\sqrt{5x}\), Now square both side of the equation. \((5\sqrt{7})^2=(\sqrt{5x})^2\) Remember to square both terms within the parentheses. Also, recall that squaring a square root sign cancels them out. \(5^2 {\sqrt{7}}^2=5x, 25(7)=5x, 175=5x, x=35\)
Best CLEP College Algebra Math Prep Resource for 2024
41- Choice C is correct
A zero of a function corresponds to an \(x\)-intercept of the graph of the function in the \(xy\)-plane. Therefore, the graph of the function \(g(x)\), which has three distinct zeros, must have three \(x\)-intercepts. Only the graph in choice C has three \(x\)-intercepts.
42- Choice B is correct
To solve for \(f(2g(P))\), first, find \(2g(p)\).
\(g(x)=log_2 x→g(p)=log_2 p→2g(p)=2log_2 p=log_2 p^2\), Now, find \(f(2g(p))\):
\(f(x)=2^x→f(log_2 p^2 )=2^{log_2 p^2} \)
Logarithms and exponentials with the same base cancel each other. This is true because logarithms and exponentials are inverse operations. Then:
\(f(log_2 p^2 )=2^{log_2 p^2 }=p^2\)
43- Choice B is correct
The slop of line A is: m\(=\frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1 }=\frac{2-(-1)}{4-2}=\frac{3}{2}\)
Parallel lines have the same slope and only choice B (\(y=\frac{3}{2} x-5\)) has a slope of \(\frac{3}{2}\).
44- Choice B is correct
Replace \(z\) by \(\frac{z}{4}\) and simplify.
\(x_1=\frac{8y+\frac{r}{r+1}}{\frac{6}{\frac{z}{4}}}=\frac{8y+\frac{r}{r+1}}{\frac{4×6}{z}}=\frac{8y+\frac{r}{r+1}}{4×\frac{6}{z}}=\frac{1}{4}×\frac{8y+\frac{r}{r+1}}{\frac{6}{z}}=\frac{x}{4}\)
When \(z\) is divided by 4, \(x\) is also divided by 4.
45- Choice A is correct
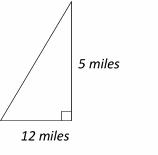
Use the information provided in the question to draw the shape.
Use Pythagorean Theorem:\(a^2+b^2=c^2 \)
\(5^2+(12)^2=c^2⇒ 25+144=c^2⇒ 169=c^2⇒ 13=c\)
46- Choice C is correct
The four-term polynomial expression can be factored completely, by grouping, as follows:
\((x^3-7x^2 )+(4x-28)=0 \)
\(x^2 (x-7)+4(x-7)=0 \)
\((x-7)(x^2+4)=0\)
By the zero-product property, set each factor of the polynomial equal to 0 and solve each resulting equation for \(x\). This gives \(x=7\) or \(x=±i\sqrt{4}\), respectively. Because the equation the question asks for the real value of \(x\) that satisfies the equation, the correct answer is 7.
47- Choice D is correct
\(0.5x=(0.25)×38→x=19→(x-3)^3=(16)^3=4,096\)
48- Choice C is correct
It is given that \(g(4)=6\). Therefore, to find the value of \(f(g(4))\), then \(f(g(4))=f(6)=5\)
49- Choice C is correct
The best way to deal with changing averages is to use the sum. Use the old average to figure out the total of the first 5 scores: Sum of first 5 scores: \((5)(80)=400\), Use the new average to figure out the total she needs after the \(6^{th}\) score: Sum of 6 scores: \((6)(82)=492\) To get her sum from 400 to 492, Mary needs to score \(492-400=92.\)
50- Choice C is correct
To solve a quadratic equation, put it in the \({ax}^2+bx+c=0\) form, factor the left side, and set each factor equal to 0 separately to get the two solutions. To solve \(2x^2=7x-3\) , first, rewrite it as\( 2x^2-7x+3=0\). Find the value of the discriminant. \(b^2-4ac=7^2-4(2)(3)=49-24=25,∆>0\), Since the discriminant is positive, the quadratic equation has two solutions \(x=3\) Or \(x=\frac{1}{2}\), There are two solutions for the equation.
51- Choice B is correct
\(y=5a^2 b-3ab+4b^2\).Plug in the values of a and b in the equation: \(a=2\) and \(b=-2\)
\(y=5(2)^2 (-2)-3(2)(-2)+4(-2)^2=-40+12+16=-12\)
52- Choice D is correct
\(f(x)=2x-8,g(x)=x^2+3x-9,\)
\((f-2g)(x)=(2x-8)-2(x^2+3x-9)=2x-8-2x^2-6x+18=-2x^2-4x+10\)
53- Choice A is correct
Let the number be A. Then: \(x=y\% ×\)A.
Solve for A. \(x=\frac{y}{100}×\)A
Multiply both sides by \(\frac{100}{y}: x×\frac{100}{y}=\frac{y}{100}×\frac{100}{y}×\)A→A\(=\frac{100x}{y}\)
54- Choice C is correct
The line passes through the origin, (8,m) and (m,18).
Any two of these points can be used to find the slope of the line. Since the line passes through (0, 0) and (8,m), the slope of the line is equal to \(\frac{m-0}{8-0}=\frac{m}{8}\). Similarly, since the line passes through (0, 0) and (m,18), the slope of the line is equal to \(\frac{18-0}{m-0}=\frac{18}{m}\). Since each expression gives the slope of the same line, it must be true that \(\frac{m}{8}=\frac{18}{m}\) , Using cross multiplication gives
\(\frac{m}{8}=\frac{18}{m}→m^2=18×8=144 →m^2=144→m=12\)
55- Choice E is correct
$1.23 per minute to use the car. This per-minute rate can be converted to the hourly rate using the conversion 1 hour \(=60\) minutes, as shown below. \(\frac{1.23}{minute}×\frac{60 minutes}{1 hours}=\frac{$(1.23×60)}{hour}\)
Thus, the car costs \($(1.23×60)\) per hour. Therefore, the cost c, in dollars, for h hours of use is c\(=(1.23×60)\)h, Which is equivalent to c\(=1.23(60\)h)
56- Choice D is correct
Plug in each pair of numbers in the equation:
A. \((-1, 2): 6(-1)-3(2)=-12\) Nope!
B. \((0, 3): 6(0)-3(3)=-9\) Nope!
C. \((1, 4): 6(1)-3(4)=6-12=-6\) Nope!
D. \((3, 2): 6(3)-3(2)=18-6=12\) Bingo!
E. \((4, 1): 6(4)-3(1)=24-3=21\) Nope!
57- Choice C is correct
Here we can substitute 8 for \(x\) in the equation. Thus, \(y-4=3(8+6), y-4=3(14)=42\) Adding 4 to both side of the equation: \(y=42+4, y=46\)
58- Choice C is correct
Let’s review the options:
I. \(|a|<1→-1<a<1\)
Multiply all sides by b. Since, \(b>0→-b<ba<b\)
II. Since,\( -1<a<1\) and \(a<0→ -a>a^2>a\) (plug in \(-\frac{1}{2}\), and check!)
III.\( -1<a<1\),multiply all sides by 4,then: \(-4<4a<4\),subtract 2 from all sides,then:
\(-4-2<4a-2<4-2→-6<4a-2<2\), I and III are correct.
59- Choice C is correct
The equation can be rewritten as \(c-d=ac\)→(divide both sides by c) \(1-\frac{d}{c}=a\), since \(c > 0\) and \(d < 0\), the value of \(-\frac{d}{c}\) is positive. Therefore, 1 plus a positive number is positive. a must be greater than 1.\( a > 1\)
60- Choice B is correct
\(f(x)=-x^3+4x^2-8x+2,g(x)=2, then f(g(x))=f(2)=-(2)^3+4(2)^2-8(2)+2=-6\)
The Best Books to Ace the CLEP College Algebra Math Test
Related to This Article
More math articles
- The Ultimate 6th Grade WVGSA Math Course (+FREE Worksheets)
- 5th Grade PSSA Math FREE Sample Practice Questions
- Top 10 8th Grade PSSA Math Practice Questions
- 4th Grade Ohio’s State Tests Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- Parent Functions
- How to Get a PhD in Math
- Full-Length 8th Grade FSA Math Practice Test-Answers and Explanations
- 6th Grade WY-TOPP Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- FREE 4th Grade STAAR Math Practice Test
- Half-Angle Identities






















What people say about "Full-Length CLEP College Algebra Practice Test-Answers and Explanations - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.